What is XSS
XSS-Cross Site Scripting
Every website(dynamic ones)’s functions are built with javascripts.
So a function such as clicking a button in a website will invoke the javascript function in the background.
But what if an attacker can input malicious javascript code into the website?
Yes this is known as Cross Site Scripting. The attacker scripts the code from the other end.
Vulnerable areas to look in a website
- Search field
- Comment boxes
- Name field
- Or any other parameter
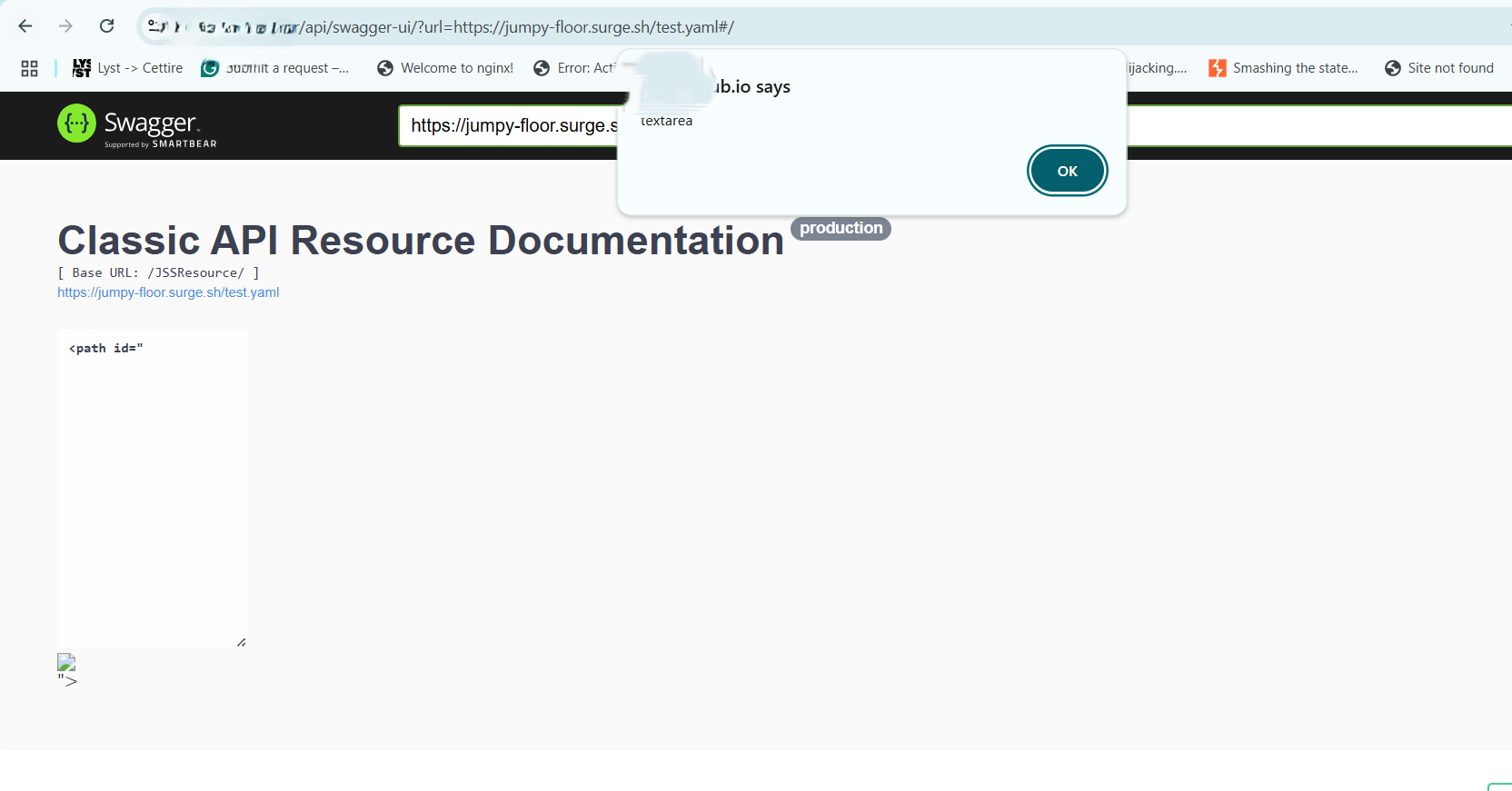
Example of cross site scripting
Imagine you’re visiting a website called example.com and find a search box on it.
You are searching for a simple query “python’” on the website
After the serach, The URL sent to the server to retrieve the results would be like:example.com/search?q="python"
But what attackers do to exploit XSS is inject ‘malicious javascript’ code such as:
<script>alert("xss")</script>
<img src=0 onerror=alert("xss")>
These malicious payloads get embedded in the source code of the website and execute on the victim’s browser to exfiltrate sensitive information from them.
Biggest Query ( What most people asked me) An Attacker performs XSS attack on the victim? But what can he truly achieve by doing so?
A popup alert box on the victim’s browser can do no harm.
This can be classified as either a low-impact or severe-impact issue for the victim.
The primary objective of a XSS attack is to get the session cookies of the victim.
The session cookies can be used by the attackers to impersonate the victims
Can’t understand the above?
Cookies (often known as internet cookies) are text files with small pieces of data — like a username and password — that are used to identify your computer as you use a network. Specific cookies are used to identify specific users and improve their web browsing experience. Data stored in a cookie is created by the server upon your connection. This data is labeled with an ID unique to you and your computer. When the cookie is exchanged between your computer and the network server, the server reads the ID and knows what information to specifically serve you. https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/definitions/cookies
in simple terms “They streamline the login information, so users don’t have to remember site passwords.” (This is the reason why,Sometimes when you log in to a website,You’re automatically logged in without authentication)
So attackers getting hands on these “cookies” will allow them to impersonate victims
But how?
every website stores session and other cookie stuff in the browser which you can view by inspecting the page(CTRL+Shift+I) and going to the ‘application` tab
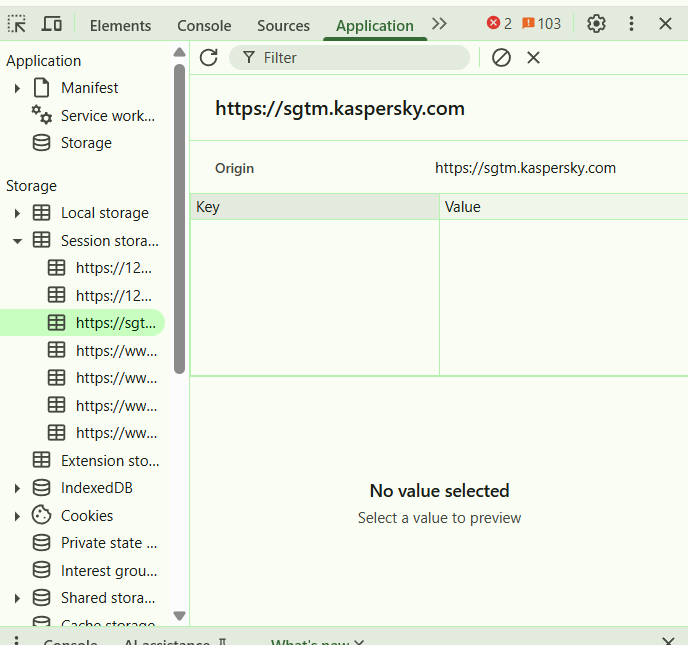
Here the attackers can place the victim’s cookie(stole from XSS) in place of his to succesfully take over the account or to access sensitive information of the victim.
Note: alert(document.cookie) will popup the victim’s cookie , The attacker can modify the payload further to send this cookie to their server.